Autonomous Cars? Really?


Autonomous driving has become a hot topic in the automotive industry over the last decade, with many car companies investing heavily in research and development to make it a reality. The promise of self-driving cars has been touted as a solution to many transportation problems, such as reducing accidents, improving traffic flow, and providing greater mobility to people who are unable to drive themselves. However, some people may wonder why car companies think that autonomous driving is possible when trains, tramways, and planes, which are also forms of transportation, have not been able to achieve this level of autonomy. In this article, we will explore the reasons behind this belief and the challenges that autonomous driving still faces.
First, it is important to understand that trains, tramways, and planes operate in very different environments than cars. Trains and tramways, for example, run on fixed rails or tracks and follow predetermined routes. They do not encounter obstacles such as pedestrians, animals, or other vehicles on their paths, which makes them much easier to control. However, trains and tramways still require a human operator to ensure their safe operation, such as monitoring the track and signaling systems, controlling speed, and making decisions in case of emergency situations.
Similarly, airplanes operate in a highly regulated and controlled environment, with air traffic controllers monitoring every flight and providing guidance to pilots. Pilots must also undergo extensive training and certification to ensure their ability to handle any situation that may arise during a flight. However, like trains and tramways, airplanes also require human operators to ensure their safe operation.
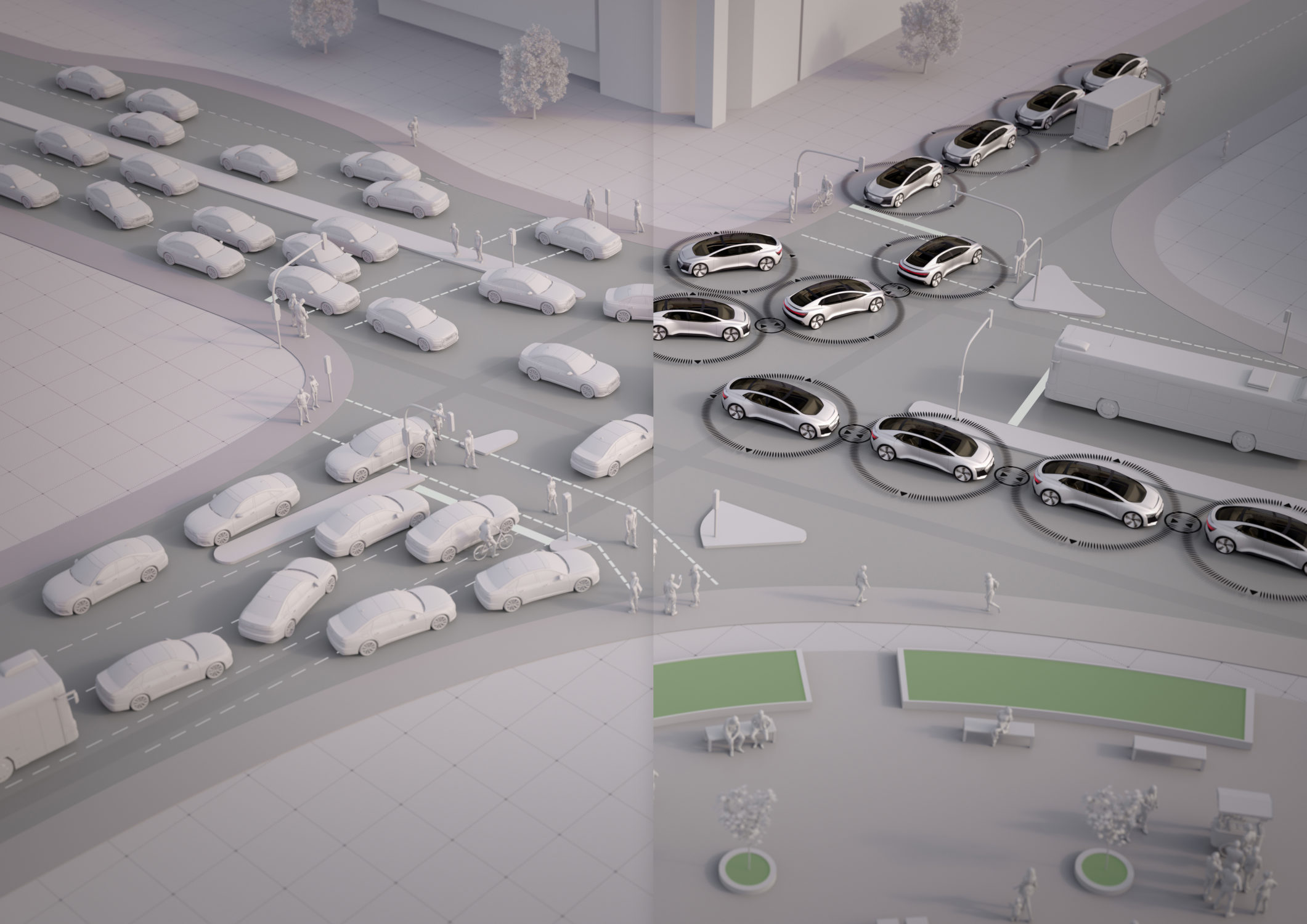

On the other hand, cars operate in a much more complex and unpredictable environment. They must navigate through a variety of situations, such as traffic congestion, changing road conditions, and unexpected obstacles. They must also interact with other drivers, pedestrians, and bicyclists who may make unpredictable or irrational decisions. These factors make autonomous driving a much more challenging task than operating trains, tramways, or planes.
Despite these challenges, car companies believe that autonomous driving is possible due to several key factors. First, advancements in technology have made it possible to equip cars with sensors, cameras, and other devices that can detect and respond to their surroundings. These systems can detect obstacles, traffic signals, and other vehicles, and make decisions about how to navigate through these situations. This technology is still developing, but it has already shown promise in reducing accidents and improving traffic flow.

Second, car companies are investing heavily in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies to improve the decision-making capabilities of autonomous cars. These systems can analyze vast amounts of data, such as real-time traffic patterns, weather conditions, and road conditions, and use this information to make more informed decisions about how to navigate through a particular situation. As these systems become more advanced, they may be able to make decisions faster and more accurately than human drivers.
Finally, car companies believe that autonomous driving can provide many benefits to society, such as reducing accidents, improving traffic flow, and providing greater mobility to people who are unable to drive themselves. Autonomous cars could also reduce the need for car ownership, as people may be able to use on-demand autonomous vehicles instead of owning their own cars. This could help reduce traffic congestion and improve air quality in urban areas.
However, despite the advancements in technology and the potential benefits, there are still significant challenges that car companies must overcome to make autonomous driving a reality. One of the main challenges is ensuring the safety of passengers and other road users. Autonomous vehicles must be able to make split-second decisions that take into account multiple factors, such as traffic, road conditions, and weather, to ensure safe operation. This requires a level of artificial intelligence that is still being developed and refined.
Moreover, the reliability of the sensors and algorithms used in autonomous driving is still a significant concern. Any errors or malfunctions could lead to accidents, which could undermine public trust in the technology. Therefore, car companies must ensure that their autonomous driving systems are thoroughly tested and validated before they are introduced to the market.
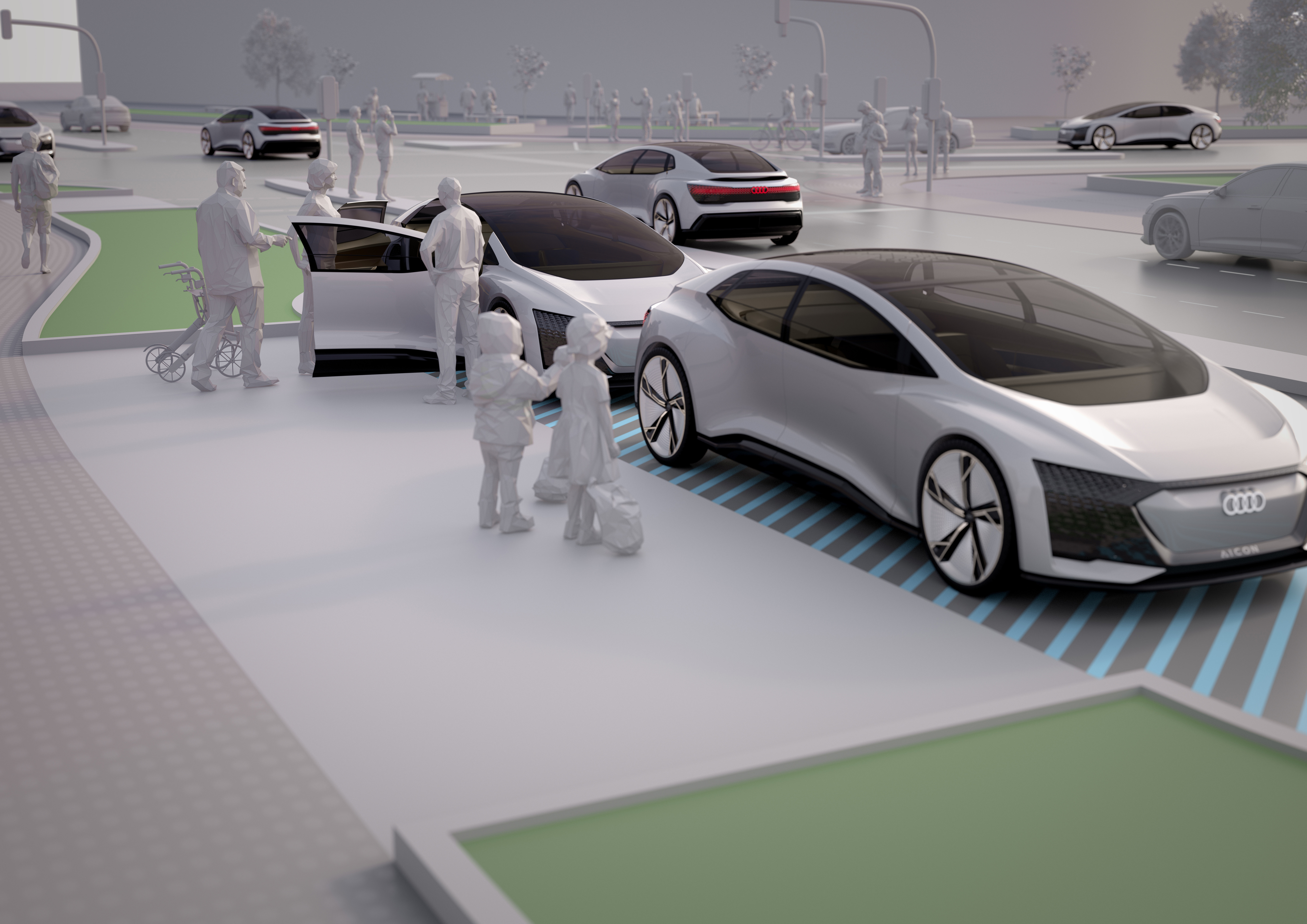

Another significant challenge is the legal and regulatory framework for autonomous driving. Many countries have yet to establish laws and regulations for autonomous vehicles, and those that have done so have different standards and requirements. This creates uncertainty for car companies, as they must navigate a complex legal landscape while trying to develop and commercialize their autonomous driving technology.
Furthermore, there are concerns about the social and economic implications of autonomous driving. For example, the widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles could lead to job losses in the transportation industry, as well as changes in land use and urban planning. Additionally, the potential for autonomous vehicles to collect and transmit vast amounts of data raises concerns about privacy and cybersecurity.
In conclusion, car companies believe that autonomous driving is possible due to the advancements in technology and the significant benefits it offers. However, there are significant challenges that must be overcome to ensure the safety and reliability of autonomous driving systems, as well as to establish a legal and regulatory framework that can support this technology. While autonomous driving may not be feasible for other modes of transportation, such as trains, trams, and planes, the unique capabilities of autonomous vehicles make them a promising solution for the future of transportation. Therefore, it is essential for car companies, policymakers, and society as a whole to work together to ensure that the potential benefits of autonomous driving can be realized while addressing the challenges and concerns.