Volkswagen AG’s Path Forward: Navigating Financial Turmoil, Restructuring, and the Future of Mobility


Once the pinnacle of automotive success, Volkswagen AG is now grappling with a confluence of challenges that threaten its financial stability, operational efficiency, and long-term competitiveness. The roots of this crisis can be traced back to the notorious Dieselgate scandal, which not only tarnished the brand’s reputation globally but also drained billions in fines, settlements, and recalls. Fast forward to 2024, and Volkswagen is struggling to find its footing amidst a rapidly shifting automotive landscape and internal strategic missteps.

The Fallout from Dieselgate
The Dieselgate scandal, unveiled in 2015, was a watershed moment for the automotive industry. Volkswagen’s deliberate manipulation of emissions tests not only eroded public trust but also led to unprecedented scrutiny of diesel vehicles worldwide. The financial repercussions were staggering—Volkswagen paid out over $30 billion in fines and legal settlements, and the incident continues to haunt the company nearly a decade later.
While other automakers diversified and adapted, Volkswagen chose a bold yet risky path: committing fully to electric vehicles (EVs). The decision to abandon internal combustion engines (ICEs) entirely was heralded as a pioneering move but one fraught with challenges. By 2023, it became evident that the transition was far more complicated and costly than anticipated.

A Fragile Foundation for Electrification
Volkswagen’s commitment to electrification was predicated on the assumption that global governments and markets would remain steadfast in their commitments to the Paris Climate Agreement of 2015. Policies banning ICE vehicles in favor of EVs seemed inevitable, but the political and economic landscape has since shifted. Several countries have postponed or diluted their emissions targets, while others are considering abandoning climate goals altogether in favor of more immediate economic priorities.
This wavering global support for clean energy transportation leaves Volkswagen in a precarious position. The company has invested heavily in EV infrastructure, factories, and technology but now faces an uncertain demand curve. Unlike Tesla, which introduced revolutionary products that redefined consumer expectations, Volkswagen’s EV lineup has been criticized for lacking distinctiveness. The vehicles neither fully reimagine the driving experience, as Tesla does, nor match the user-friendly design and competitive pricing of rivals like Hyundai, Kia, Mercedes-Benz, or BMW.

Overlapping Brands and Competing Portfolios
Volkswagen’s multi-brand strategy is another key contributor to its current woes. With brands like Volkswagen, Audi, Porsche, Skoda, SEAT, Bentley, and Lamborghini, the group boasts one of the most diverse automotive portfolios in the world. However, this diversity has increasingly become a liability. Many of these brands offer overlapping products that compete directly with one another, resulting in unnecessary cannibalization and inefficiencies.
The variety of drivetrain technologies across the group further complicates matters. Volkswagen continues to produce plug-in hybrids, mild hybrids, ICE vehicles, and battery electric vehicles (BEVs), all within the same brand families. This lack of focus has led to higher costs, slower production cycles, and diluted investments. While diversification has its advantages, Volkswagen appears to be spreading itself too thin, failing to dominate any single market segment.

Financial Strain and Operational Cuts
To compound matters, Volkswagen’s restructuring efforts have highlighted the depth of its financial struggles. The company has announced factory closures and significant layoffs as it attempts to cut costs and stabilize its operations. These measures, while necessary, risk alienating employees, damaging morale, and affecting production output.
The layoffs are particularly concerning for Volkswagen’s EV push. EVs require fewer components and less labor to produce than ICE vehicles, but this efficiency comes at the expense of job losses. With unions playing a significant role in European automotive manufacturing, these reductions may lead to further tensions and disruptions.

Suggestions for Steering Volkswagen in the Right Direction
While the situation is dire, Volkswagen’s extensive resources and storied history offer a foundation for recovery. To navigate this crisis, the company must focus on the following strategies:
1. Rethink the Multi-Brand Strategy
Volkswagen must streamline its portfolio by reducing redundancies between brands. Each brand should have a clear identity and target audience. For example, Skoda and SEAT could focus on affordable, mass-market vehicles in emerging markets, while Volkswagen and Audi could refine their offerings for mid-tier and premium consumers. Luxury brands like Porsche, Bentley, and Lamborghini should focus on high-margin, niche markets with cutting-edge performance and technology.
2. Prioritize Profitability in the Transition to Electrification
Rather than phasing out ICE vehicles entirely, Volkswagen should adopt a more pragmatic approach. Retain ICE vehicles in markets where EV adoption remains slow due to infrastructure challenges or affordability concerns. Simultaneously, accelerate the development of cost-effective EVs that can compete with Hyundai and Kia on price and user-friendliness.
3. Focus on Differentiated EV Design
Volkswagen must break away from the “safe” designs of its current EV lineup. Consumers are drawn to EVs not only for their environmental benefits but also for their innovative features and aesthetics. Tesla succeeded by redefining the driving experience; Volkswagen must do the same. This could involve integrating intuitive user interfaces, advanced autonomy features, and bold designs that capture the imagination of consumers.
4. Optimize EV Production Costs
Volkswagen’s current EV pricing makes it less competitive in key markets. By simplifying production processes and focusing on modular architectures like the MEB platform, Volkswagen can achieve economies of scale. Additionally, vertical integration in battery manufacturing could reduce costs while securing supply chains.
5. Rebuild Trust Through Transparency
The shadow of Dieselgate still looms large. Volkswagen must double down on corporate social responsibility, sustainability, and ethical business practices. This includes transparency in emissions data, supply chain management, and executive decision-making.
6. Adapt to Regional Markets
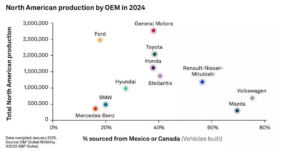
A one-size-fits-all approach will not work in today’s fragmented global market. Volkswagen must tailor its product offerings to meet the unique needs of each region. For example, EVs may be prioritized in Europe and China, while hybrids and ICE vehicles remain the focus in North America and developing markets.
7. Invest in Mobility Solutions
The future of the automotive industry extends beyond vehicle sales. Volkswagen should expand its investments in mobility solutions, including car-sharing, subscription services, and autonomous driving technology. These initiatives can diversify revenue streams and position Volkswagen as a leader in future mobility.

Conclusion: A Crossroads for Volkswagen
Volkswagen AG’s challenges are emblematic of an industry undergoing rapid transformation. The company’s current predicament underscores the importance of balancing bold innovation with pragmatic strategy. By streamlining its operations, refining its EV offerings, and rebuilding trust, Volkswagen has the opportunity to reclaim its position as a global automotive leader. However, the road ahead will require difficult decisions, disciplined execution, and a renewed focus on the evolving needs of consumers and markets. If Volkswagen can navigate these challenges, it may yet turn this crisis into an opportunity for reinvention and growth.